Filter by category:
Filter by group:
 | Essence (alchemy) One of the signs in alchemy and early chemistry for essence. |
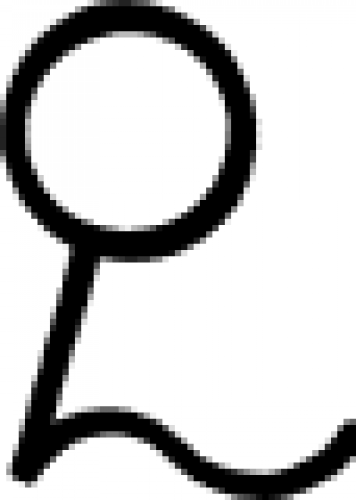 | Quintessence (alchemy) In the context of alchemy, the word "quintessence" can refer to a number of different things, some of them rather esoteric in nature. |
 | Digestion (alchemy) In alchemy, digestion is a process in which gentle heat is applied to a substance over a period of several weeks. |
 | Multiplication (alchemy) Multiplication is the process in Western alchemy used to increase the potency of the philosopher's stone, elixir or projection powder. |
 | Spiritus (alchemy) This ancient symbol can have many different meanings, but in the context of alchemy it represents spiritus. |
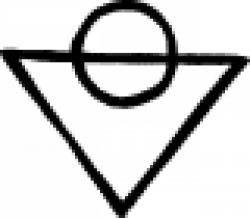 | Salt water (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to represent salt water. |
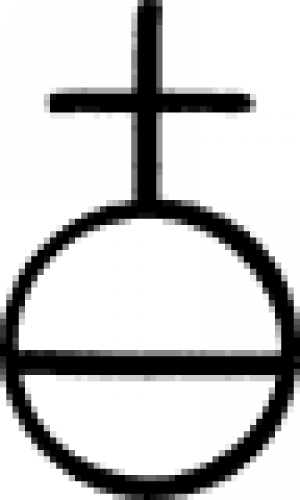 | Cinnabar of Antimony (alchemy) A symbol used to designate Vermillion Dye (Mercuric Sulfide), a bright red pigment with a rather toxic physical nature, in 17th century alchemy. |
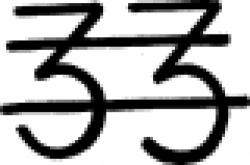 | Cinnabar (Alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy and early chemistry to represent cinnabar. |
 | Retort (alchemy) The device represented by this symbol symbol is also known as an "alembic" or "distillery tube" and plays an import role the discipline of alchemy. |
 | Fixation (alchemy) Fixation in alchemy refers to a process by which a previously volatile substance is "transformed" into a form (often solid) that is not affected by fire. |
 | Projection (alchemy) Projection was the ultimate goal of Western alchemy. Once the Philosopher's stone or powder of projection had been created, the process of projection would be used to transmute a lesser substance int… |
 | Potash (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to represent potash. |
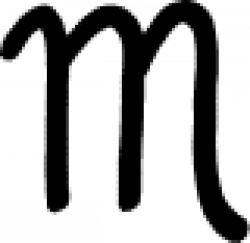 | Transform into liquid (alchemy) Bearing some resemblance to the astrological sign for Scorpio, in alchemy this symbol indicates that something is transformed into a liquid. |
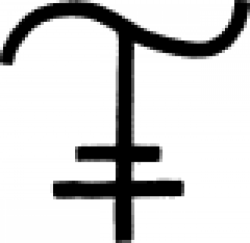 | Limestone (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to represent limestone. |
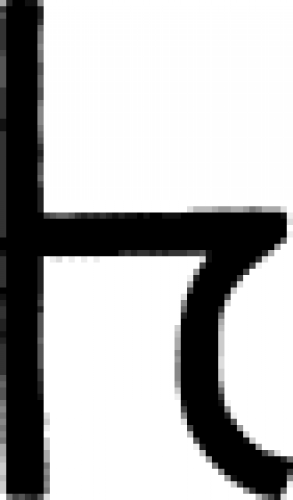 | Lapis lazuli (alchemy) A sign used in alchemy for lapis lazuli. |
 | Pebbles (alchemy) A sign in alchemy used to represent pebbles. It can also stand for the colorless variety of quartz known as rock crystal. |
 | Hot fire (alchemy) A sign used in alchemy to represent a particularly intense flame. |
 | Fool's gold (alchemy) Fool's gold, or iron pyrite, is represented in alchemy by this symbol. |
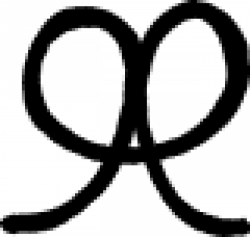 | Potassium hydrogen tartrate (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to denote potassium hydrogen tartrate. |
 | Rubber (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to indicate rubber or resin. |
 | Week (alchemy) A time sign used in alchemy to indicate a week. |
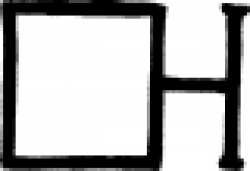 | Rock salt (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to designate rock salt. |
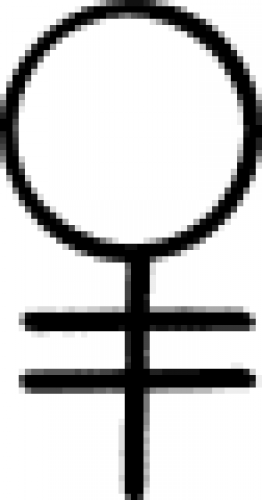 | Brass (alchemy) A sign used in alchemy to represent the metal brass. |
 | Glass (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to designate glass. |
 | Forge (alchemy) A sign used in alchemy to indicate a forge or melting oven. |
 | Night (alchemy) One of several "time signs" used both in alchemy and early chemistry, this one representing night. |
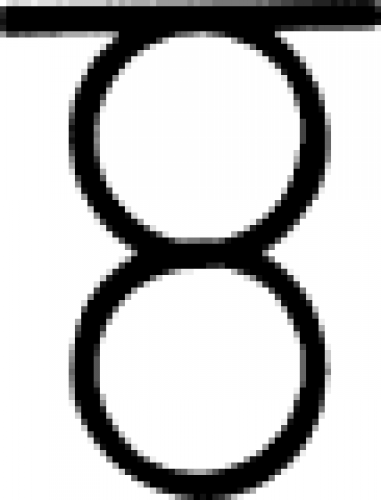 | Melting (alchemy) A sign used in alchemy to indicate melting or digestion. |
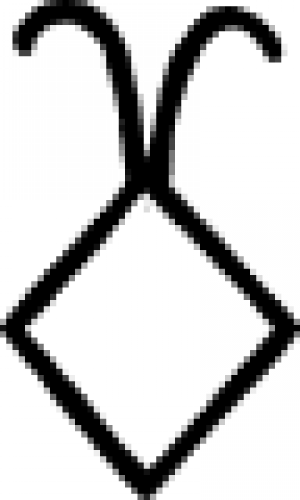 | Soap (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to represent soap. |
 | Vitriol (alchemy) One of several symbols used in alchemy to represent vitriol. |
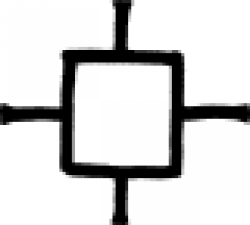 | Ink (alchemy) In alchemy and early chemistry, this symbol represented ink. |
 | Preserve or burn (alchemy) In alchemy, this symbol can have two distinctive meanings. |
 | Wax (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to denote wax or oil. |
 | Calcinated copper (alchemy) A sign used in 17th century alchemy to designate calcinated copper. |
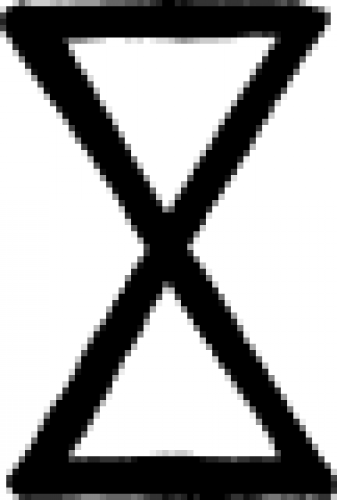
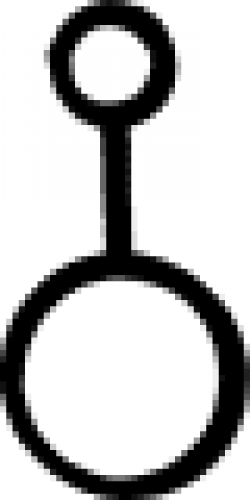 | Nickel (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to indicate the metal nickel. |
 | Hour (alchemy) One of several "time signs" used in alchemy to indicate the period of an hour. |
 | Juice or sap (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to indicate juice or sap. |
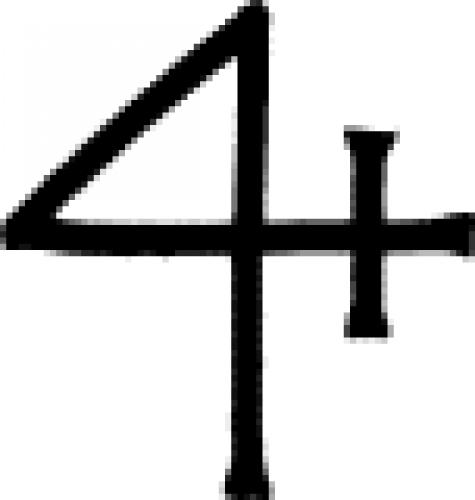 | Borax (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy and early chemistry to represent borax. |
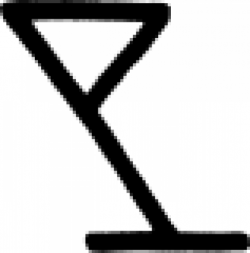 | Crucible (alchemy) Resembling a lopsided martini glass, this symbol was used in alchemy to indicate a crucible or a melting pot. |
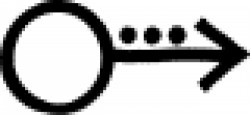 | Iron filings (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to indicate iron filings. |
 | Rotting (alchemy) A sign used in alchemy to indicate the process of rotting, or putreficatio. |
 | Melt (alchemy) A sign used in alchemy to indicate melting, fusion or making something into a liquid form. |
 | Glue (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy to indicate glue. |
 | Cobalt (alchemy) A symbol used in alchemy and early chemistry to represent cobalt, alkali salt and rock salt. |
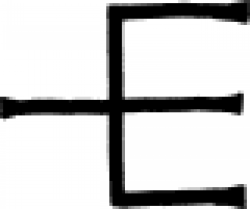 | Ash (alchemy) A sign representing ash in the alchemical tradition. |
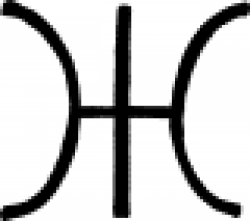 | Ammonium salt (alchemy) One of the alchemical signs for ammonium salt, also known as "sal ammoniacus". |
 | Precipitation (alchemy) Resembling an upside-down version of the astrological symbol for Libra, this alchemical sign represents precipitation. |
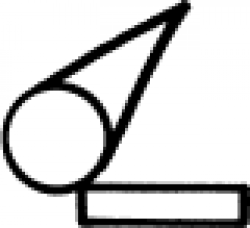 | Gold-leaf (alchemy) An alchemical symbol for gold-leaf. |
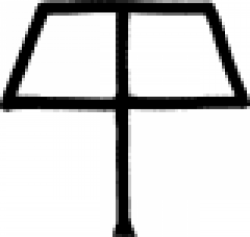 | Stone (alchemy) and working people This symbol denotes two specific things in two different fields. |
 | Gold foil (alchemy) An alchemical symbol used to indicate gold foil, or "aurum foliatum". |
 | Purification (alternate) or setting (alchemy) An alchemical symbol that represents both purification and setting. |
 | Purification (alchemy) The sign for purification, or "purificatio", combines the symbols for 'water' (squiggly lines) and 'vessal' (bowl shape). |
 | Winter (alchemy) The alchemical sign for winter. |
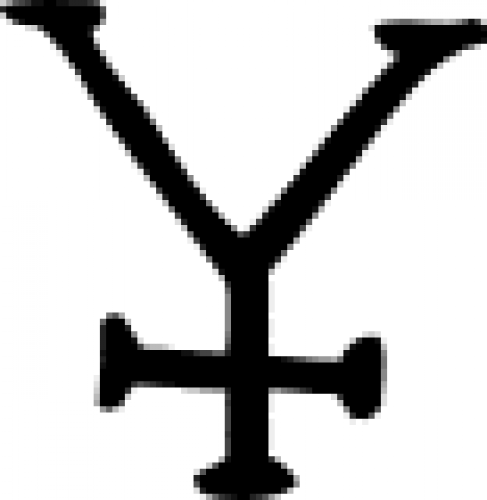 | Metal (alchemy) A general alchemical sign indicating metal. |
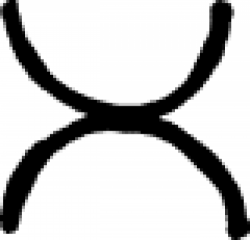 | Decoction (alchemy) An old alchemical sign for decoction. |
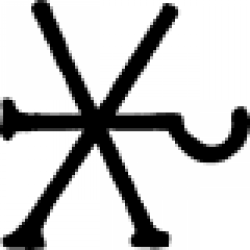 | Summer (alchemy) One of the time signs used by alchemists, this one representing summer. |
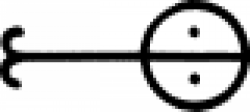 | Hydrochloric acid (alchemy) The alchemical symbol for hydrochloric acid. |
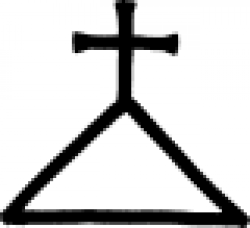 | Phosphorus (alchemy) The alchemical symbol for phosphorus. |
 | Ferrohydrosulphate (alchemy) This rather tongue-twisting moniker indicates a combination of iron and sulphur. |
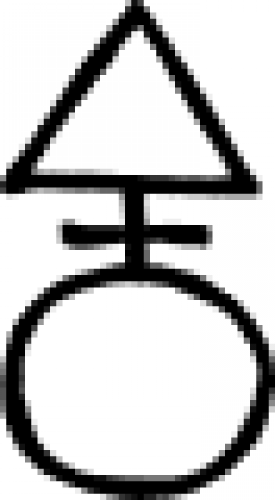 | Steel (alchemy) The alchemical symbol for steel. |
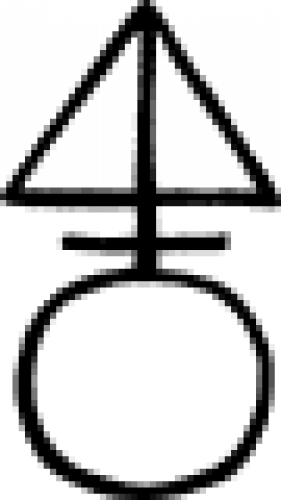 | Ferrum sulphuratum (alchemy) The alchemical symbol for ferrum sulphuratum, a compound of iron and sulphur. |
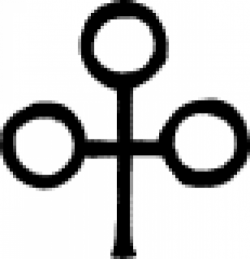 | Cuprum arsenicatum (alchemy) The alchemical symbol for Cuprum arsenicatum, a compound of copper and arsenic. |
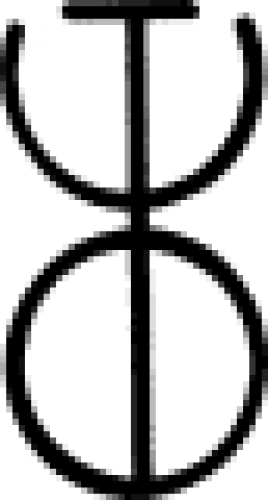 | Salt (alchemy) One of several alchemical signs for sodium chloride (i.e. salt). |
 | Wood (alchemy) An alchemical symbol representing wood. |
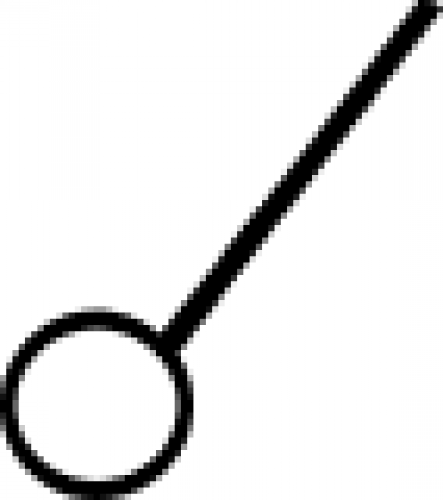 | Day (alchemy) While this symbol can have different meanings in different fields, in the alchemical traditions of the Middle Ages it was used as a "time sign" to indicate day. |
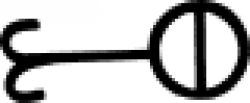 | Nitric acid (alchemy) An alchemical symbol for nitric acid. |
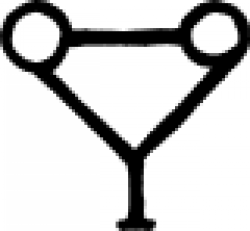 | Horse dung (alchemy) A symbol used by alchemists to represent horse dung. |
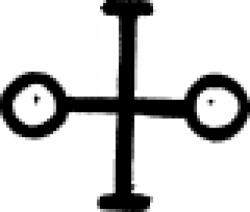 | Arsenic acid (alchemy) The alchemical and early chemical symbol for arsenic acid, or acidum arsenici. |
 | Process (alchemy) When it comes to this symbol, the word "process" can imply a number of different things. |
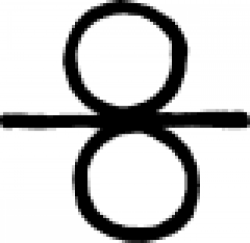 | Year (alchemy) One of several alchemical "time signs" used to indicate the period of a year. |
 | Molten gold (alchemy) The alchemical symbol for something known as "aurum cum caloric", possibly molten gold. |
 | Antimony oxide (alchemy) The alchemical symbol for antimony oxide. |
 | Aurum musivum (alchemy) This alchemical substance, also known as stannum sulphuratum, is a compound of tin and sulphur. |
 | Ammonia (alchemy) A symbol used in 18th century chemistry to indicate ammonia. |
 | 24 hours (alchemy) Combining the discipline's own symbols for day and night, this alchemical time sign represents a period of 24 hours. |
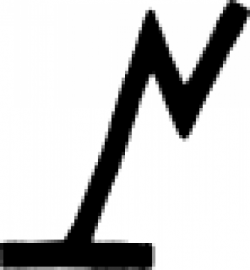 | Cement (alchemy) A symbol from 17th century chemistry indicating cement or putty. |
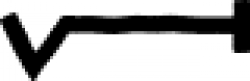 | Natron (alchemy) A symbol from 17th century chemistry used to indicate natron. |
 | White lead (alchemy) An early chemical symbol used to indicate white lead. |
 | Mix (alchemy) An alchemical symbol indicating the process of mixing. |
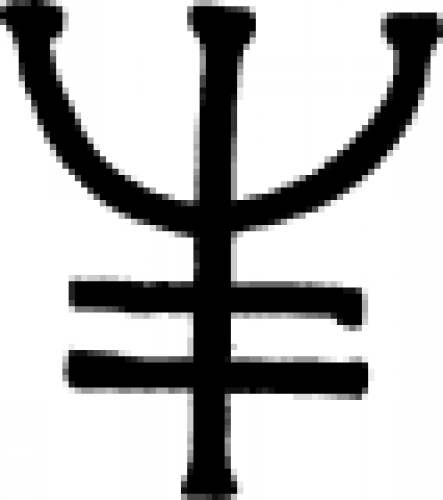 | Magnesia\Magnesium (alchemy) Resembling a trident, this sign is a 16th century chemical symbol for magnesia. |
 | Lime (alchemy) A symbol used to represent lime in early chemistry. |
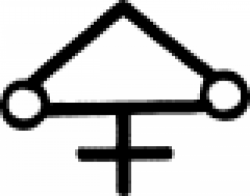 | Arsenic sulphate (alchemy) An alchemical and early chemical symbol for the compound arsenic sulphate. |
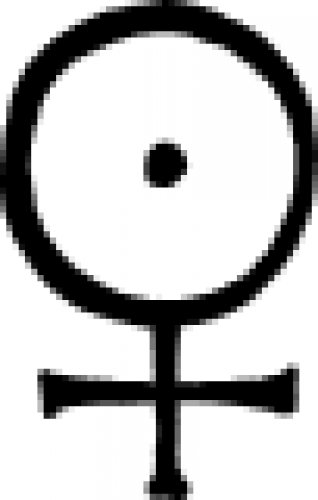 | Gilded copper (alchemy) An 18th century symbol representing gilded copper, or cuprum auratum. |
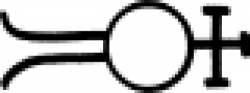 | Alcohol (alchemy) An early chemical symbol used to indicate alcohol or a wine spirit. |
 | Zinc (alchemy) An 18th century chemical symbol representing the metal zinc. |
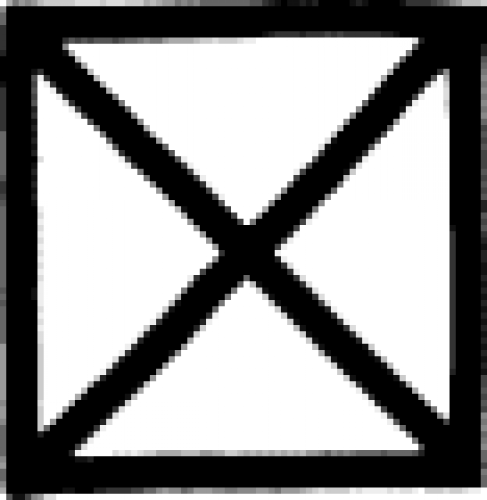 | Month (alchemy) An alchemical "time sign" used to indicate the period of a month. |
 | Spring (alchemy) An alchemical sign for spring. |
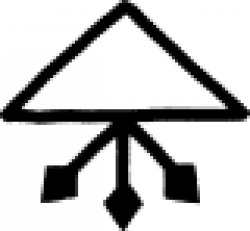 | Wise man's sulphur (alchemy) A symbol used in 17th century chemistry to indicate a substance known as wise man's sulphur, or "soufre des philosophes" |
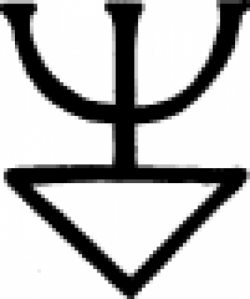 | Hepar calcis (alchemy) An 18th century symbol for hepar calcis, more commonly known today as calcium sulfide (chemical symbol- CaS). |
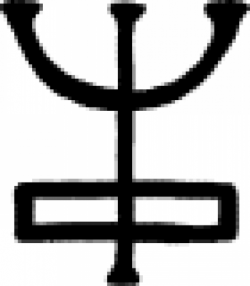 | Terra ponderosa (alchemy) A symbol from 18th century chemistry. |
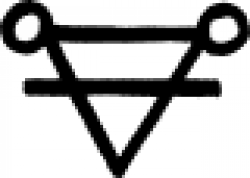 | Clay (alchemy) An 18th century chemical symbol for clay (also known as 'agrilla'). |
 | Coal (alchemy) A symbol used to represent coal (also known as 'carbo') in 18th century chemistry. |
 | Wind furnace (alchemy) An alchemical symbol indicating a wind furnace (also known as a wind forge). |
 | Melting furnace (alchemy) One of several alchemical symbols used to indicate a melting furnace. |
 | Hot water (alchemy) An alchemical symbol indicating hot or warm water. |
 | Saffron (alchemy) A symbol occasionally used by alchemists to indicate saffron. |
 | Zinc oxide (alchemy) A symbol used to indicate zinc oxide in chemical practices of the 18th and 19th centuries. |
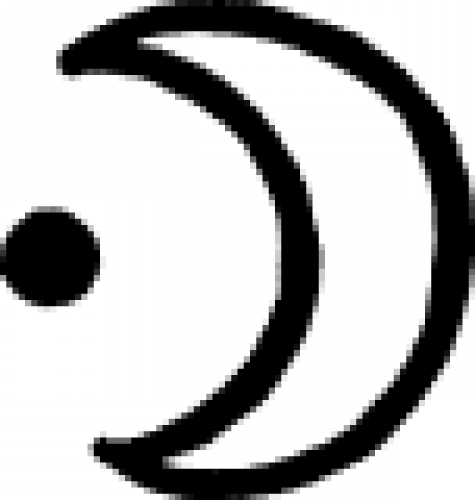 | Gilded silver (alchemy) An 18th century symbol representing gilded silver, or argentum auratum. |
 | Pulverize (alchemy) An 18th century chemical symbol used to indicate the process of pulverizing ("pulverisare") and the result of that process, powder ("pulvis") |
 | Fuse (alchemy) An 18th century chemical symbol indicating the process of fusing, or melting things together. |
 | Nitrogenous air (alchemy) An 18th century chemical symbol used to indicate nitrogen dioxide and other similar gasses. |
 | Quicklime (alchemy) An early chemical symbol used to indicate quicklime, also known as calcium oxide. |
 | Pyrophorus (alchemy) An 18th century chemical symbol indicating pyrophorus. |
 | Lye\alkali (alchemy) An alchemical symbol used to indicate lye. |
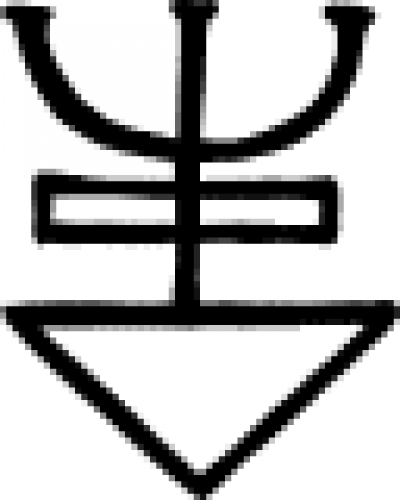 | Hepar terraepond (alchemy) An 18th century chemical symbol representing hepar terraepond, Barium Sulfide, "hepar" being Latin for 'liver', "terræpond" short for "Terra Ponderosa," the name of the first recognized ores of Bariu… |
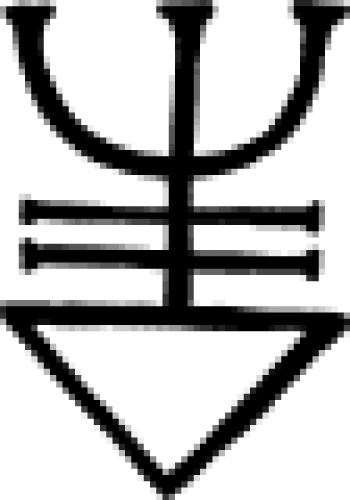 | Hepar magnesiae (alchemy) An 18th century chemical symbol representing hepar magnesiae, now known as Magnesium Sulfide, "hepar" being Latin for 'liver,' because of the red colors of some sulfides. |
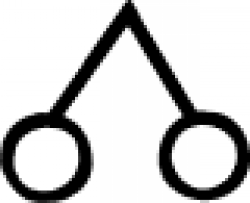 | Magnetic iron or rising (alchemy) An alchemical symbol that can indicate either magnetic iron or the process of rising. |
 | Strain (alchemy) An alchemical symbol indicating the process of filtration or straining. |
 | Arsenic sulphide (alchemy) A 17th century chemical symbol for arsenic sulphide, also known as auripigmentum or orpiment, mineral As₂S₃. |
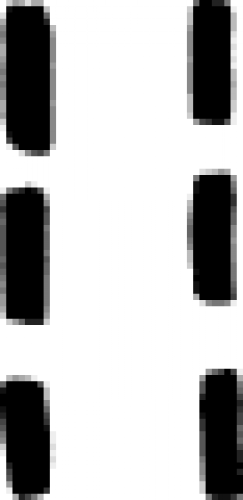 | Evaporation (alchemy) An 18th century chemical symbol for evaporation. |
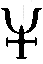 | Calx (Alchemy) An ambiguous term for lime or for a metallic oxide. |
 | Quintessence (alternate) In the context of alchemy, the word "quintessence" can refer to a number of different things, some of them rather esoteric in nature. |
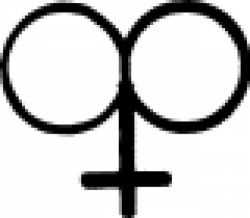
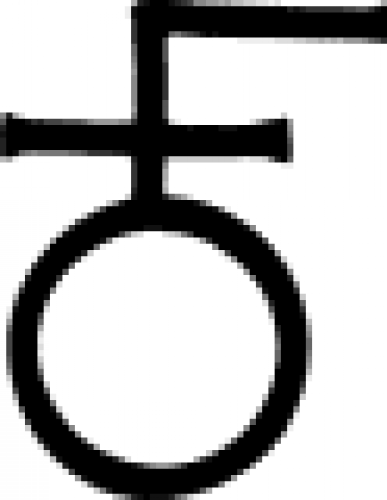
 | Copper Alchemy symbol for copper. This was also the symbol for the goddess and the planet Venus. |
 | Goddess Alchemy symbol for goddess. It was also the symbol for copper and the planet Venus. |
 | Spiritus (alternate #1) This ancient symbol can have many different meanings, but in the context of alchemy it represents spiritus. |
 | Amalgam (alternate) In alchemy, an amalgam is a combination of two different metals. |
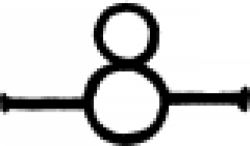 | Spiritus (alternate #2) In the context of alchemy, this symbol represents spiritus. |
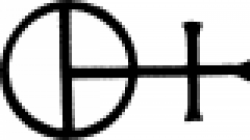 | Red vitriol The symbol used in alchemy and early chemistry to represent red vitriol. |
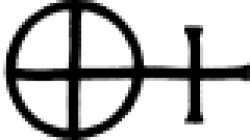 | Blue vitriol The symbol used in alchemy and early chemistry to represent blue vitriol. |
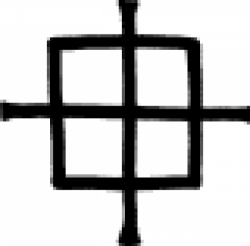 | Iron vitriol The symbol used in alchemy and early chemistry to represent iron vitriol. |
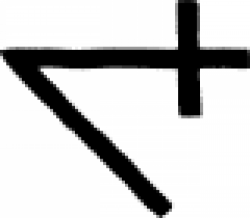 | Wax (alternate #3) or coagulation In the practice of alchemy, this symbol can have two distinct meanings. |
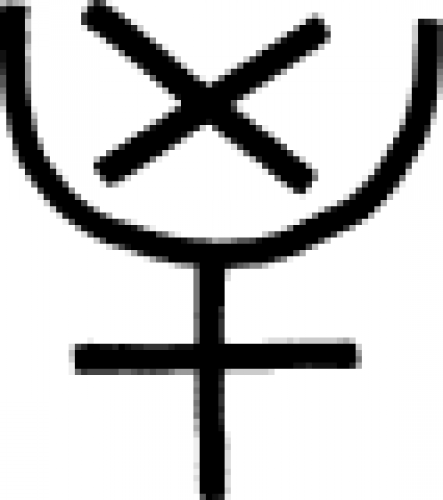 | Fixation (alternate) A symbol used in alchemy to represent the process of fixation. |
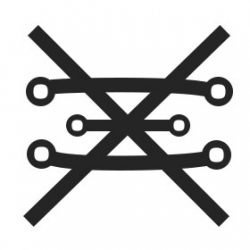 | Copper An ancient alchemy symbol representing copper. |
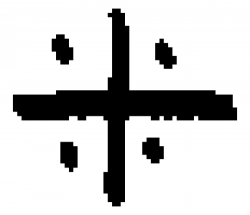
 | Ceration Ceration is a chemical process, a common practice in alchemy. |
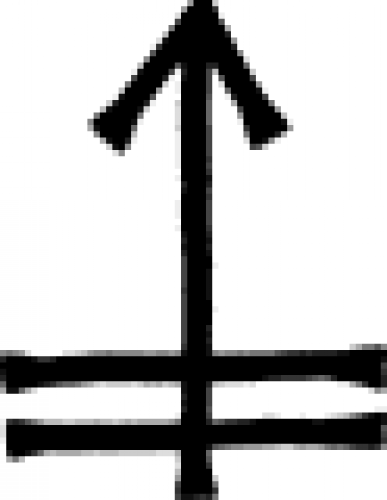
 | Distilled vinegar An old alchemy symbol for distilled vinegar. |
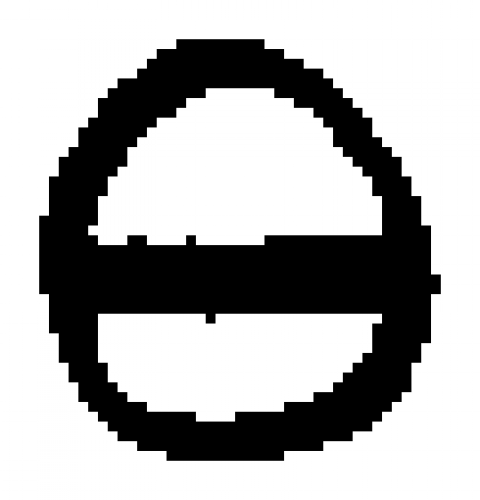 | Salt An old alchemy symbol that symbolizes Salt. |
 | Oil An old archaic alchemy symbol for oil. |
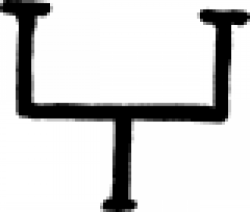
 | Iron (alternate #1) A symbol for iron in alchemy and early chemistry. |
 | Potash (alternative) A symbol used in alchemy to represent potash. |
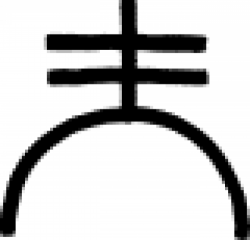 | Amalgam In alchemy and chemistry, an amalgam is an alloy of mercury and another metal or ammonia |
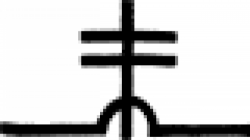 | White arsenic In alchemy, white arsenic is an oxide used to create a color known as Schweinfurt green. |
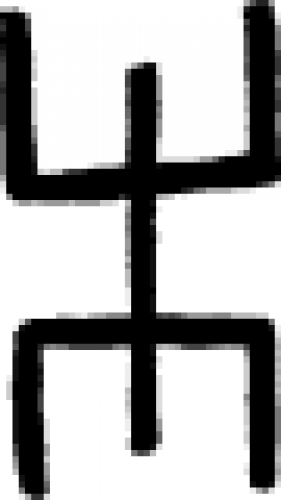 | Sand One of the signs for "sand" or "arena" in alchemy and early chemistry. |
 | Transform into liquid (alternate) Bearing some resemblance to the astrological sign for Aquarius (which it functions as a version of), in alchemy this symbol indicates that something is transformed into a liquid. |
 | Aqua regia This mixture of two different acids was an important substance in the practice of alchemy. |
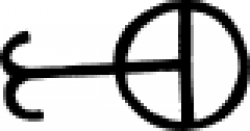 | Aqua regia (alternate) This mixture of two different acids was an important substance in the practice of alchemy. |
 | Fool's gold (alternate) Fool's gold, or iron pyrite, is represented in alchemy by this symbol. |
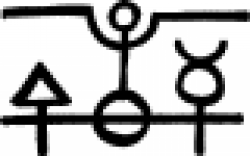 | Philosopher's Stone The philosopher's stone, or lapis philosophorum ('stone of wisdom'), is perhaps the most iconic object in the study of alchemy. |
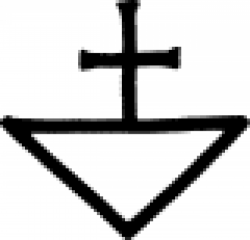 | Philosopher's Stone (alternate) The philosopher's stone, or lapis philosophorum ('stone of wisdom'), is perhaps the most iconic object in the study of alchemy. |
 | Talc In alchemy and chemistry, this symbols denotes the substance talc. |
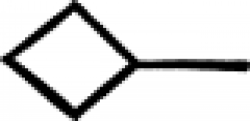 | Rock salt (alternate) A symbol used in alchemy to designate rock salt. |
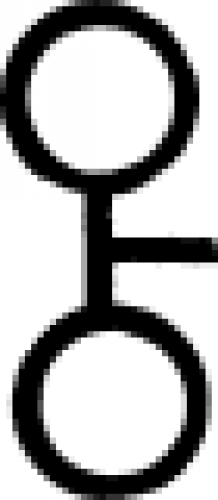 | Arsenic (alternate #1) One of many symbols used in alchemy to designate arsenic. |
 | Arsenic (alternate #2) One of many symbols used in alchemy to designate arsenic. |
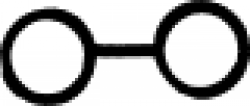 | Arsenic (alternate #3) or glass One of many symbols used in alchemy to designate arsenic. |
 | Arsenic (alternate #4) One of many symbols used in alchemy to designate arsenic. |
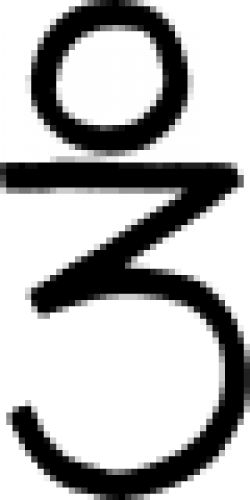 | Arsenic (alternate #5) One of many symbols used in alchemy to designate arsenic. |
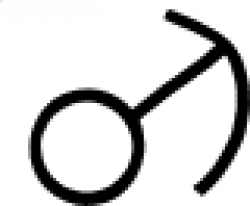 | Arsenic (alternate #6) One of many symbols used in alchemy to designate arsenic. |
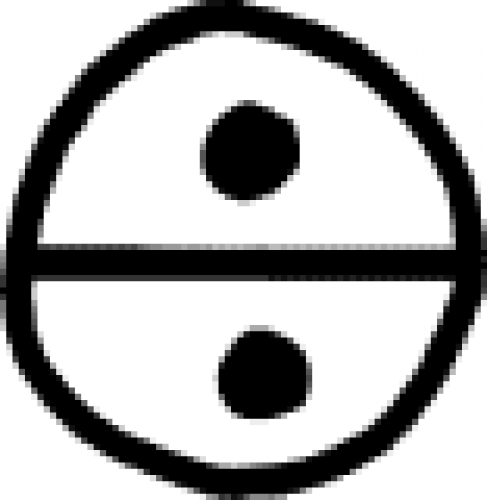 | Sal alcalinus A symbol used in alchemy to indicate alkaline salt, which is composed of sodium and potassium. |
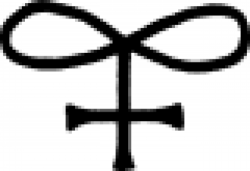 | Glass (alternate #1) A symbol used to represent glass in medieval alchemy. |
 | Wood (alternate #1) While at first glance this symbol may be mistaken for a warped version of the anarchy logo, it is in fact one of the symbols used in alchemy to denote wood. |
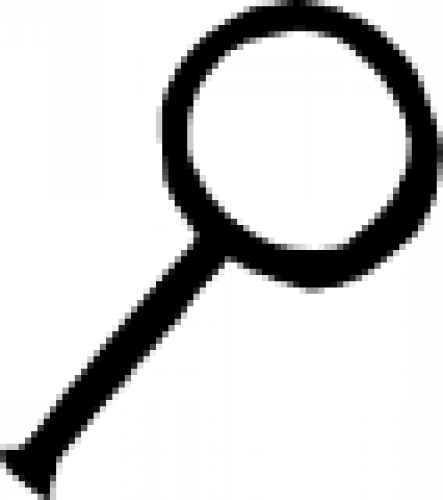
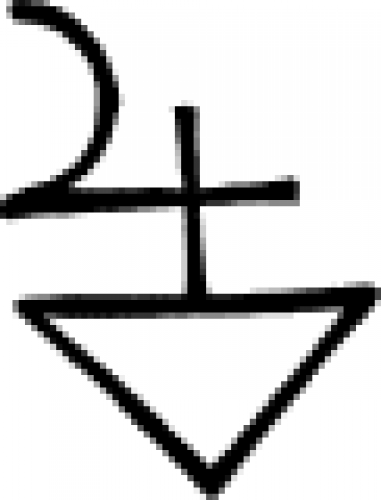
 | Mars (alternate) Although this sign isn't often used, in alchemy it is an alternative symbol to indicate the planet Mars. |
 | Iron (alternate #2) A symbol for iron in alchemy and early chemistry. |
 | Iron (alternate #3) A symbol for iron in alchemy and early chemistry. |
 | Iron (alternate #4) A symbol for iron in alchemy and early chemistry. |
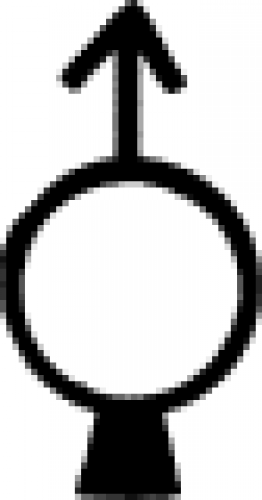 | Iron (alternate #5) A symbol for iron in alchemy and early chemistry. |
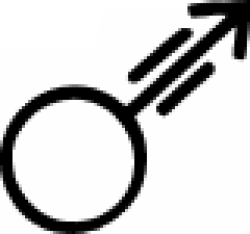 | Iron (alternate #6) A symbol for iron in alchemy. |
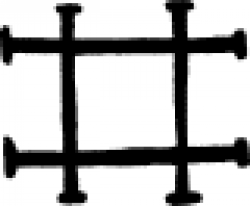 | Lead (alternate #1) In alchemy, lead is most commonly represented by the astrological sign for the planet Saturn (for full details, see the symbol for 'Lead'), but this symbol serves the same purpose. |
 | Lead (alternate #2) In alchemy, lead is most commonly represented by the astrological sign for the planet Saturn (for full details, see the symbol for 'Lead'), but this symbol serves the same purpose. |
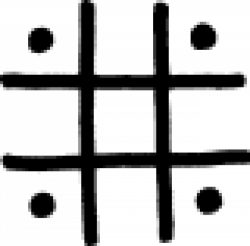 | Acetic acid\vinegar (alternate #1) One of several symbols used in alchemy and early chemistry to denote vinegar. |
 | Acetic acid\vinegar (alternate #2) A sign used in 17th century alchemy to indicate a distilled form of vinegar. |
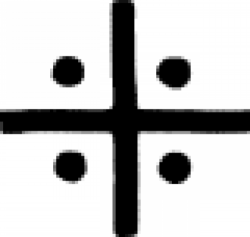
 | Wax (alternate #1) A symbol used in alchemy to denote wax or oil. |
 | Oil (alternate #5) An symbol used in 17th century alchemy to designate oil. |
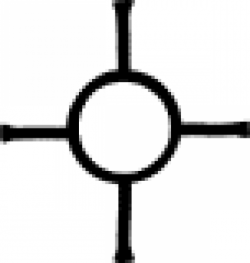
 | Wax (alternate #2) A symbol used in alchemy to indicate wax or olive oil. |
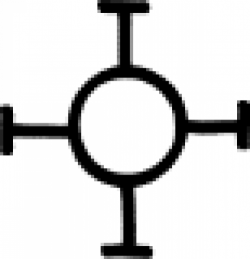
 | Calcinated copper (alternate #1) A sign used in 17th century alchemy to designate calcinated copper. |
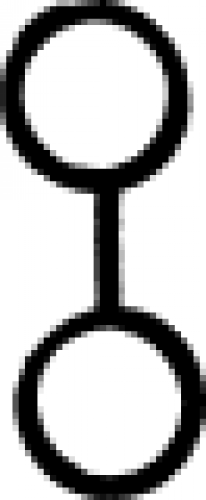 | Calcinated copper (alternate #3) or nickel In alchemy, this symbol could indicate either calcinated copper or the metal nickel. |
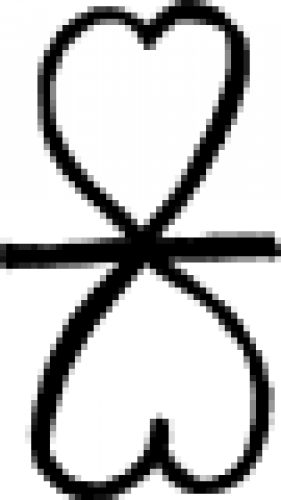 | Hour (alternate #2) One of several "time signs" used in alchemy to indicate the period of an hour. |
 | Lead (alternate #3) In alchemy, lead is most commonly represented by the astrological sign for the planet Saturn (for full details, see the symbol for 'Lead'), but this symbol serves the same purpose. |
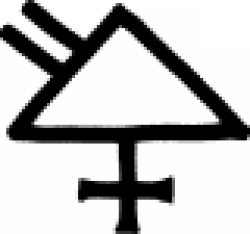 | Arsenic (alternate #7) One of many symbols used in alchemy to designate arsenic. |
 | Aqua fortis (alternate) A symbol used in alchemy to indicate aqua fortis, better known as nitric acid. |
 | Crucible (alternate #1) Resembling a sealed envelope, this symbol was used in alchemy to indicate a crucible or a melting pot. |
 | Calcination (alternate) One of several symbols used in alchemy to represent calcination. |
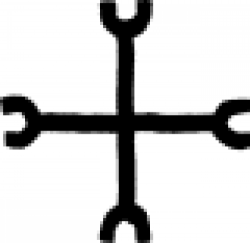 | Vinegar (alternate) In Christianity, this type of sign is known as a crutch cross. In alchemy it is one of several signs indicating vinegar. |
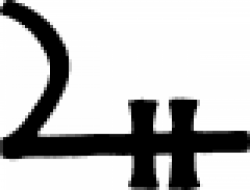 | Steel (alternate #1) One of several symbols used in alchemy to represent steel. |
 | Lead (alternate #4) In alchemy, lead is most commonly represented by the astrological sign for the planet Saturn (for full details, see the symbol for 'Lead'), but this symbol serves the same purpose. |
 | Year (alternate #1) One of several "time signs" used in alchemy and early chemistry to indicate the period of a year. |
 | Night (alternate) One of several "time signs" used in alchemy, this one representing night. |
 | Sal alcalinus (alternate #1) A symbol used in alchemy to indicate alkaline salt, which is composed of sodium and potassium. |
 | Lead (alternate #5) In alchemy, lead is most commonly represented by the astrological sign for the planet Saturn (for full details, see the symbol for 'Lead'), but this symbol serves the same purpose. |
 | Vitriol (alternte) One of several symbols used in alchemy to represent vitriol. |
 | Hot fire (alternate) A sign used in alchemy to represent a particularly intense flame. |
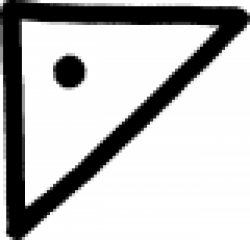 | Lead (alternate #6) In alchemy, lead is most commonly represented by the astrological sign for the planet Saturn (for full details, see the symbol for 'Lead'), but this symbol serves the same purpose. |
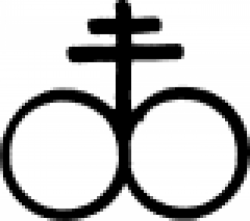 | Black sulphur or brimstone A symbol that represents black sulphur (aka black mercuric sulphide), as well as brimstone, in alchemy. |
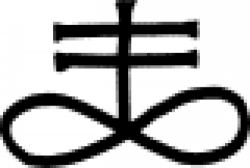 | Black sulphur or brimstone (alternate) A symbol that represents black sulphur (aka black mercuric sulphide), as well as brimstone, in alchemy. |
 | Vinegar (alternate #4) One of several symbols used in alchemy to denote vinegar. |
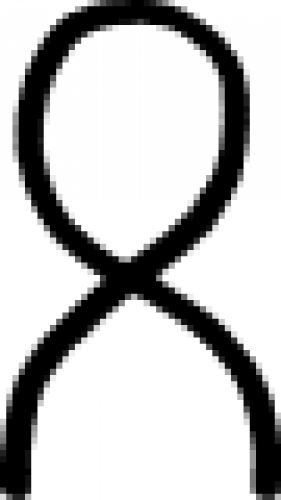 | Sal alcalinus (alternate #3) A symbol used in alchemy to indicate alkaline salt, which is composed of sodium and potassium. |
 | Melting (alternate) A sign used in alchemy to indicate a flow or melting. |
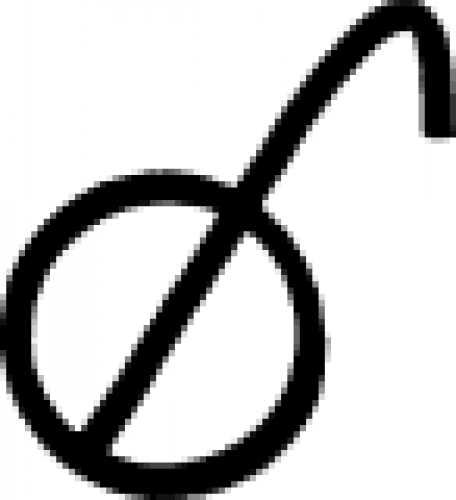 | Lead (alternate #7) In alchemy, lead is most commonly represented by the astrological sign for the planet Saturn (for full details, see the symbol for 'Lead'), but this symbol serves the same purpose. |
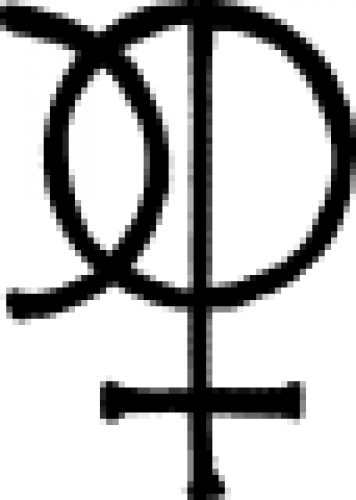 | Oricalchum argentatum In alchemy, oricalchum argentatum is a name for brass that has been coated in silver. |
 | Circulation, Alchemical Process Alchemical process of circulation as seen on the Wheel of Fortune Trump in Robert Place's excellent Alchemical Tarot. |
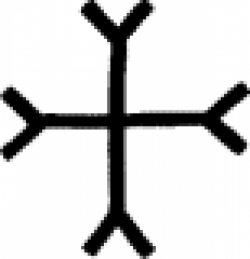 | Anchor Cross (alternate #1) or White lead This symbol, which can take several different forms, is a variation of the Christian cross. |
 | The eight-pointed star The eight-pointed star appears in cultures around the globe. Eight pointed stars – show up in a variety of different cultures. |
 | Venus Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days.The planet is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. |
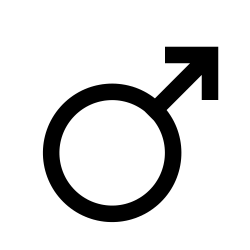 | Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second smallest planet in the Solar System. Named after the Roman god of war, it is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on … |
 | Caduceus The caduceus (☤; pron.: /kəˈdjuːsiːəs/ or /kəˈdjuːʃəs/; from Greek κηρύκειον kērukeion "herald's staff" ) is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology. |
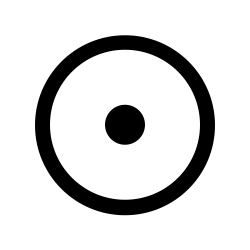 | Gold Gold, often described as a dense, soft, shiny, malleable, and ductile metal, has captivated human imagination for millennia. Its allure lies not only in its physical properties but also in its symbol… |
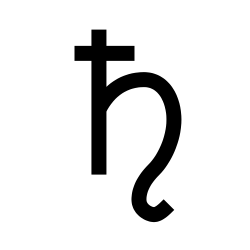 | Lead Lead is a chemical element in the carbon group with symbol Pb (from Latin: plumbum) and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft and malleable metal, which is regarded as a heavy metal and poor metal. |
 | Mercury (metal) Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is commonly known as quicksilver and was formerly named hydrargyrum (from Greek "hydr-" water and "argyros" silver). |
 | Calcination Calcination (also referred to as calcining) is a thermal treatment process in absence of air applied to ores and other solid materials to bring about a thermal decomposition, phase transition, or rem… |
 | Congelation Congelation is the process by which something congeals, or thickens. |
 | Sublimation (phase transition) Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase. |
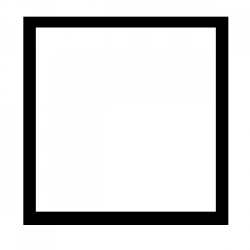 | Square In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. This means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle in which two… |
 | Pearl Although pearls are not technically 'stones' in the way many other gems are, they still carry a wealth of symbolic meaning. In certain cultures, these beauties are accorded particularly high status, … |
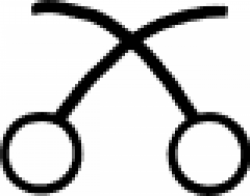 | Realgar (alternate #2) or Smoke One of several alchemical symbols for realgar. |
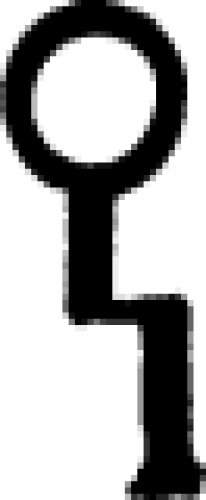 | Cinnabar (alternate #1) A symbol used to designate cinnabar, a bright red mineral with a rather toxic physical nature, in the 18th century text of Diderot's Encyclopedia. |
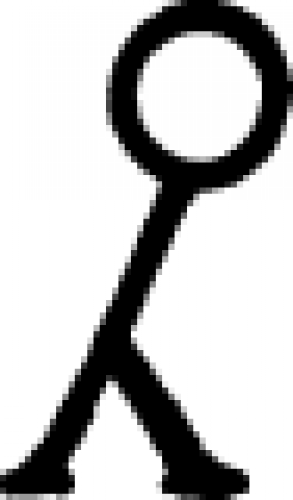 | Cinnabar (alternate #2) A symbol used to designate cinnabar, a bright red mineral with a rather toxic physical nature, in the 18th century text of Diderot's Encyclopedia. |
 | Purify by burning In alchemical practices, this symbol represents a purification process. |
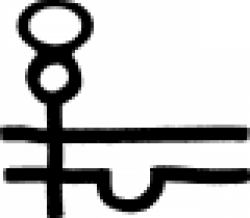 | White Precipitate (Alternate #2) Resembling a combination of the signs for Precipitation and Mercury, this alchemical symbol represents either of two insoluable compounds, Mercuric Amide Chloride (HgNH2Cl2) "Infusible white precipit… |
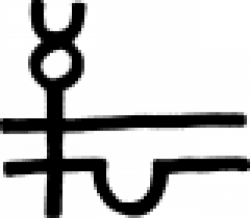 | White Precipitate Resembling a combination of the signs for Precipitation and Mercury, this alchemical symbol represents either of two insoluable compounds, Mercuric Amide Chloride (HgNH2Cl2) "Infusible white precipit… |
 | Precipitation (alternate #1) One of several alchemical symbols for precipitation, in this case precipitation from solution. |
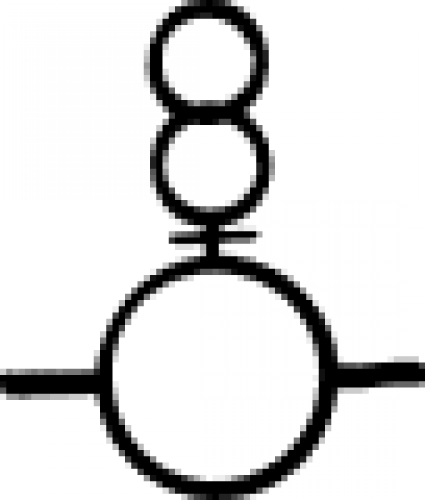 | White Precipitate (alternate #3) An early chemical symbol for the white powder created by putting corrosive sublimate in a solution of ammonia or sal ammoniac. |
 | Yellow Rose Perhaps the most famous of all flowers, the rose has been a prominent symbol for many millennia. The facets of this flower’s symbolic meaning are almost innumerable, but one of the easiest ways to ca… |
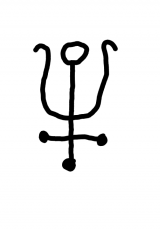 | The Grey Wolf\Antimony The Fourth Step of procuring The Philosopher's Stone |
 | Fermentation, Alchemical Process The alchemical process of Fermentation (AKA Fermentatio). As seen on the "Strength" trump of Robert Place's excellent Alchemical Tarot. |
 | Disposition, Alchemical Process Alchemical process of Disposition. As seen on the "Justice" trump of Robert Place's excellent Alchemical Tarot. |
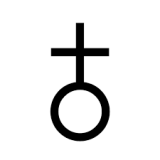 | The Earth, Alchemical Symbol Alchemical symbol for The Earth, our planet, as opposed to the element earth. AKA "The World" in alchemical terms. |
 | Dissolution, Alchemical Process The alchemical process of Dissolution as peculiarly represented by the symbol for Aquarius. |

