Astronomical Symbols Page #2
This page lists all the various symbols in the Astronomical Symbols category.
Astronomical symbols are symbols used to represent various celestial objects, theoretical constructs and observational events in astronomy. The earliest forms of these symbols appear in Greek papyri of late antiquity. The Byzantine codices in which the Greek papyri were preserved continued and extended the inventory of astronomical symbols. New symbols were further invented to represent many just-discovered planets and minor planets discovered in the 18th-20th centuries.
Symbols in this category:
3 Juno
Juno, minor-planet designation 3 Juno in the Minor Planet Center catalogue system, was the third asteroid to be discovered and is one of the larger main-belt asteroids, being one of the two largest stony (S-type) asteroids, along with 15 Eunomia.
3 Juno
Juno, minor-planet designation 3 Juno in the Minor Planet Center catalogue system, was the third asteroid to be discovered and is one of the larger main-belt asteroids, being one of the two largest stony (S-type) asteroids, along with 15 Eunomia.
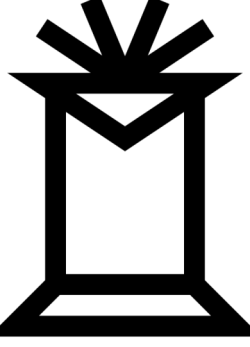
37 Fides
37 Fides (pron.: /ˈfaɪdiːz/ FY-deez) is a large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German astronomer Karl Theodor Robert Luther on October 5, 1855, and named after Fides, the Roman goddess of loyalty. Fides was the last of the main-belt asteroids to be assigned an iconic symbol.
4 Vesta
Vesta, minor-planet designation 4 Vesta, is one of the largest asteroids in the Solar System, with a mean diameter of 525 kilometers (326 mi).
4 Vesta
Vesta, minor-planet designation 4 Vesta, is one of the largest asteroids in the Solar System, with a mean diameter of 525 kilometers (326 mi).
4 Vesta
Vesta, minor-planet designation 4 Vesta, is one of the largest asteroids in the Solar System, with a mean diameter of 525 kilometers (326 mi).
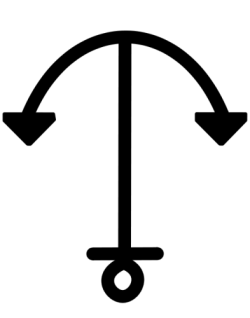
5 Astraea
5 Astraea is a large main-belt asteroid. Its surface is highly reflective (bright) and its composition is probably a mixture of nickel-iron with magnesium- and iron-silicates.
5 Astraea
5 Astraea is a large main-belt asteroid. Its surface is highly reflective (bright) and its composition is probably a mixture of nickel-iron with magnesium- and iron-silicates.
6 Hebe
6 Hebe (pron.: /ˈhiːbiː/ HEE-bee) is a large main-belt asteroid, containing around half a percent of the mass of the belt.
6 Hebe
6 Hebe (pron.: /ˈhiːbiː/ HEE-bee) is a large main-belt asteroid, containing around half a percent of the mass of the belt.
7 Iris
7 Iris is a large main-belt asteroid. Among the S-type asteroids, it ranks fifth in geometric mean diameter after Eunomia, Juno, Amphitrite and Herculina.
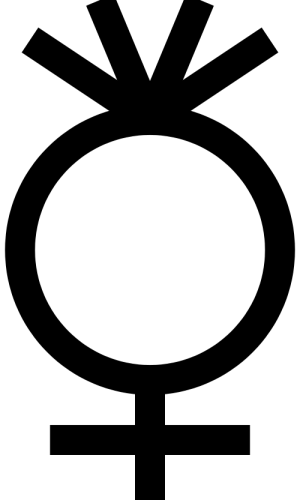
Ceres
Ceres, minor-planet designation 1 Ceres, is the only dwarf planet in the inner Solar System, and the largest asteroid. It is a rock–ice body 950 km (590 mi) in diameter, and the smallest identified dwarf planet. It contains about one third of the mass of the asteroid belt. Discovered on 1 January 1801 by Giuseppe Piazzi, it was the first asteroid to be identified, though it was classified as a planet at the time. It is named after Ceres, the Roman goddess of growing plants, the harvest, and motherly love.
Comet
A comet is an icy small Solar System body (SSSB) that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma (a thin, fuzzy, temporary atmosphere) and sometimes also a tail.
Citation
Use the citation below to add this symbols category to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"Astronomical Symbols." Symbols.com. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 23 Nov. 2024. <https://www.symbols.com/category/34/Astronomical+Symbols>.










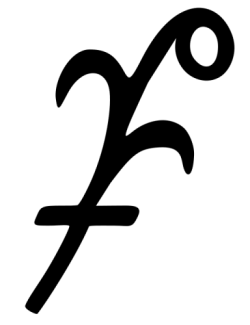


Have a discussion about the Astronomical Symbols category with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In