Electrical & Electronic Symbols
This page lists of the various symbols in the Electrical & Electronic Symbols group.
An electronic symbol is a pictogram used to represent various electrical and electronic devices (such as wires, batteries, resistors, and transistors) in a schematic diagram of an electrical or electronic circuit. These symbols can (because of remaining traditions) vary from country to country, but are today to a large extent internationally standardized. Some symbols represent components which ceased to be used routinely as newer technologies were introduced (such as vacuum tubes).
Symbols in this group:
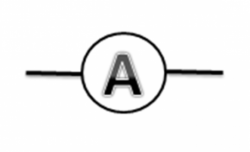
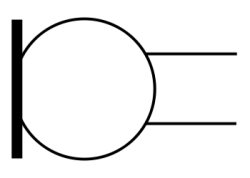
Ammeter Symbol
An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the electric current in a circuit.
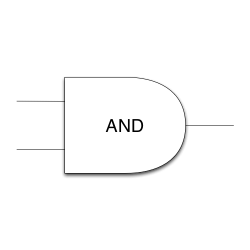
AND gate
An AND gate is a digital logic gate that performs the "AND" function on two inputs, that is, the output is HIGH(1) if both inputs are HIGH(1).
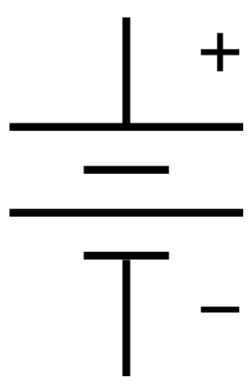
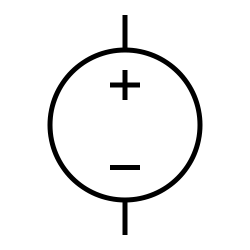
Battery
The symbol for a battery in a circuit diagram. It originated as a schematic drawing of the earliest type of battery, a voltaic pile.
Capacitor
A capacitor (originally known as condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field.
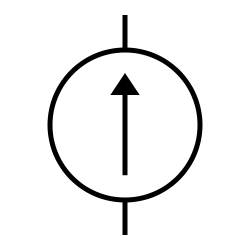
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.
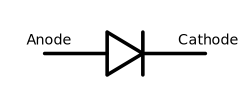
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a two-terminal electronic component with an asymmetric transfer characteristic, with low (ideally zero) resistance to current flow in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. A vacuum tube diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a plate (anode) and heated cathode.
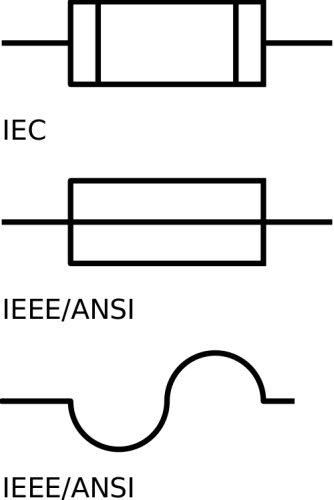
Fuse
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse (from the French fuser, Italian fuso, "spindle") is a type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to provide overcurrent protection, of either the load or source circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows, which interrupts the circuit in which it is connected. Short circuit, overloading, mismatched loads or device failure are the prime reasons for excessive current.
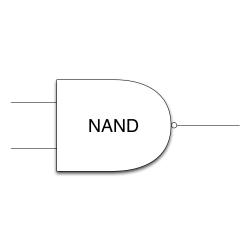
NAND gate
A NAND gate is the equivalent of an AND gate with a NOT gate on the output. The output of a NAND gate is HIGH(1) as long as both inputs are not HIGH(1).
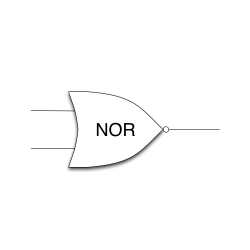
NOR gate
A NOR gate is the equivalent of an OR gate with a NOT gate on its output. The output of NOR gate is only HIGH(1) if both of its inputs are LOW(0).
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.
The Electronic Switch Symbol
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another.
The Inductor Symbol
An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it.
Voltage source
Voltage source is a two terminal device which can maintain a fixed voltage.
Citation
Use the citation below to add this symbols group page to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"Electrical & Electronic Symbols." Symbols.com. STANDS4 LLC, 2025. Web. 22 Jan. 2025. <https://www.symbols.com/group/8/Electrical+%26%2338%3B+Electronic+Symbols>.



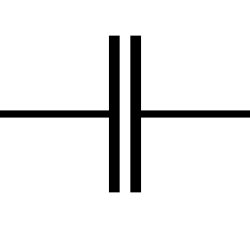






Have a discussion about the Electrical & Electronic Symbols group with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In