Alphabets
This page lists of the various symbols in the Alphabets group.
An alphabet is a standard set of letters (basic written symbols or graphemes) which is used to write one or more languages based on the general principle that the letters represent phonemes (basic significant sounds) of the spoken language. This is in contrast to other types of writing systems, such as syllabaries (in which each character represents a syllable) and logographies (in which each character represents a word, morpheme or semantic unit).
Symbols in this group:
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet (Arabic: أَبْجَدِيَّة عَرَبِيَّة ’abjadiyyah ‘arabiyyah) or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.
ASL Letter Vv
American Sign Language and the sign that has now become unanimous with victory or peace.
Bǎikē quánshū (simplified)
Chinese characters representing "Bǎikē quánshū", which translates as 'Encyclopedia'.
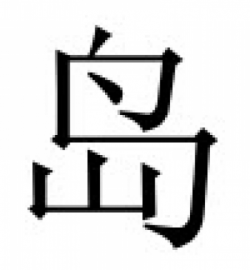
Biānniánshǐ
Chinese characters representing "Biānniánshǐ", which translates as 'Chronicle' or 'Annals'.
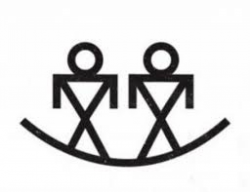
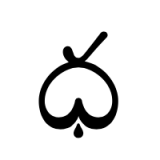
Brothers Symbol
The Brothers symbol is depicted in almost every creation story among the Native American Indians.
Cháhuā (simplified)
Chinese characters representing "Cháhuā", which translates as 'Camellia'.
Daleth (South Arabian alphabet)
The letter "d" as rendered in the South Arabian alphabet.
Dòufu
Chinese characters representing "Dòufu", which can be translated as either 'Tofu' or 'Bean curd'.
English alphabet
The modern English alphabet is a Latin alphabet consisting of 26 letters.
Gimel (South Arabian alphabet)
The letter "g" as rendered in the South Arabian alphabet.
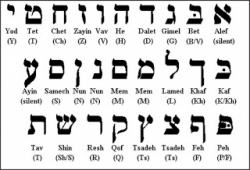
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet (alefbet ʿIvri ), known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian alphabet, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two script forms in use. The original old Hebrew script is known as the paleo-Hebrew script (which has been largely preserved, in an altered form, in the Samaritan script), while the present "square" form of the Hebrew alphabet is a stylized form of the Assyrian script. Various "styles" (in current terms, "fonts") of representation of the letters exist. There is also a cursive Hebrew script, which has also varied over time and place.
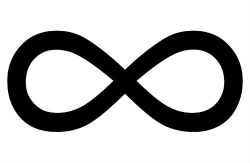
Infinity Symbol
The infinity symbol (sometimes called the lemniscate) is a mathematical symbol representing the concept of infinity.
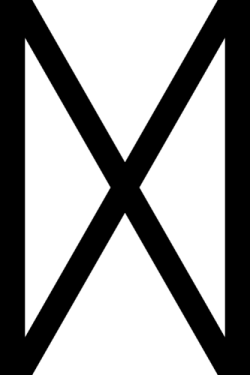
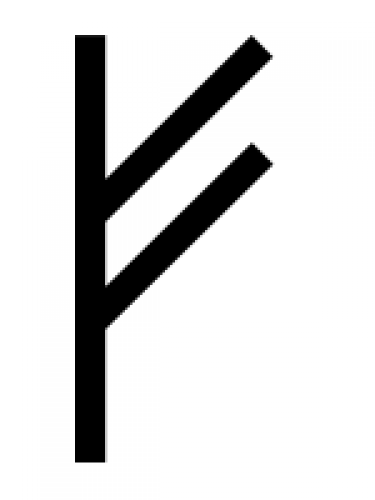
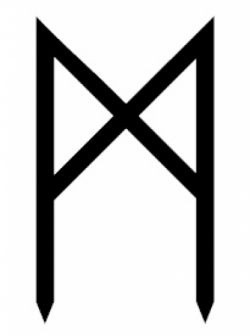
Ing - Ingz - Ingwaz
The twenty-second letter of Futhark is Ingwaz. This rune represents Ing, the god of the fertility and the creative act.
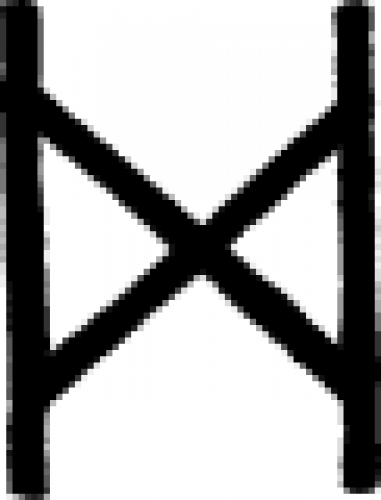
Laguz
*Laguz or *Laukaz is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the l-rune ᛚ, *laguz meaning "water" or "lake" and *laukaz meaning "leek".
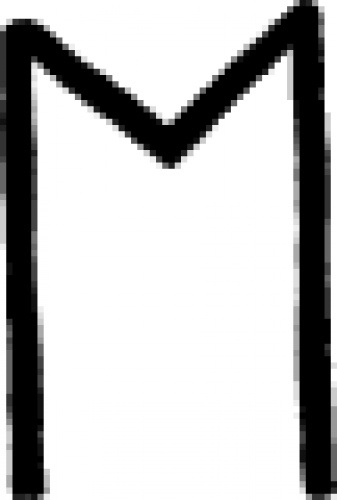
Lamdeh (South Arabian alphabet)
The letter "l" as rendered in the South Arabian alphabet.
LEET SYMBOL ጷ - Ethiopic Syllable Phwa (U+1337) symbol, character
LEET SYMBOL ጷ - Ethiopic Syllable Phwa (U+1337) symbol, character this character is typed by pressing alt+1337 on Windows machines or Ctrl+Alt+u1337 on Linux Machines
Niú
Chinese character representing "Niú", which can be variously translated as 'Ox', 'Cow' or 'Bull'.
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1200 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia. It is classified as an abjad because it records only consonantal sounds (matres lectionis were used for some vowels in certain late varieties).
Pi (letter)
Pi (/ˈpaɪ/; Greek: [pi], uppercase Π, lowercase π) is the sixteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing [p]. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 80. It was derived from the Phoenician letter pe Phoenician pe.svg. Letters that arose from pi include Cyrillic Pe (П, п), Coptic pi (Ⲡ, ⲡ), and Gothic pairthra (
psi
Psi is the 23rd letter of the Greek alphabet and has a numeric value of 700. In both Classical and Modern Greek, the letter indicates the combination /ps/ (as in English word "lapse")
Pútáo
Chinese characters representing "Pútáo", which translates as 'Grapes' (can also indicate the singular 'Grape').
Rì chū (simplified)
Chinese characters representing "Rì chū", which translates as 'Sunrise'.
Russian alphabet
The Russian alphabet (Russian: русский алфавит, transliteration: rússkij alfavít) is a form of the Cyrillic script, developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School. The modern Russian alphabet consists of 33 letters.
Sa (kana)
さ, in hiragana, or サ in katakana, is one of the Japanese kana, which each represent one mora. Both represent [sa]. The shapes of these kana originate from 左 and 散, respectively.
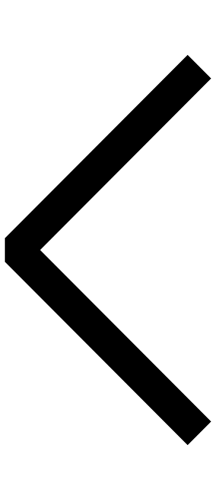
Samekh (South Arabian alphabet)
The letter "s" as rendered in the South Arabian alphabet.
Shin
Shin (also spelled Šin (šīn) or Sheen) literally means "tooth", "press", and "sharp"; It is the twenty-first letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician Shin Phoenician Hebrew Shin ש, Aramaic Shin Syriac Shin ܫ, and Arabic Shin ش (in abjadi order, 13th in modern order). Its sound value is a voiceless sibilant, [ʃ] or [s].
Suǒ zi jiǎ
Chinese characters representing "Suǒ zi jiǎ", which translates as 'Chainmail'.
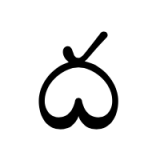
The Phoenix Symbol
In Greek mythology, a phoenix or phenix (Ancient Greek φοίνιξ phóinīx) is a long-lived bird that is cyclically regenerated or reborn. Associated with the sun, a phoenix obtains new life by arising from the ashes of its predecessor. The phoenix was subsequently adopted as a symbol in Early Christianity.
Tiějiàng (simplified)
Chinese characters representing "Tiějiàng", which translates as 'Blacksmith'.
Wind furnace (process, #1)
An alchemical symbol that indicates to process something in a wind furnace.
Xiāngcài
Chinese characters representing "Xiāngcài", which can be translated as either 'Parsley' or 'Coriander'.
Yāpiàn (simplified)
Chinese characters representing "Yāpiàn", which translates as 'Opium'.
Yèyīng (simplified)
Chinese characters representing "Yèyīng", which can be translated as 'Nightingale' or, more generally, 'Bulbul' (referring to a family of the Passerine order of birds).
Zhāngyú (simplified)
Chinese characters representing "Zhāngyú", which translates as 'Octopus'.
Æ ae ligature
Æ is a grapheme named æsc or ash, formed from the letters a and e, originally a ligature representing the Latin diphthong ae.
Citation
Use the citation below to add this symbols group page to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"Alphabets Symbols." Symbols.com. STANDS4 LLC, 2025. Web. 22 Feb. 2025. <https://www.symbols.com/group/47/Alphabets>.
























































































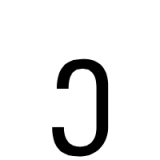












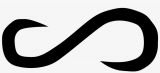






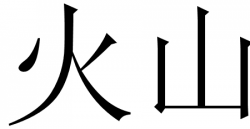




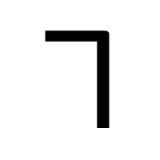



















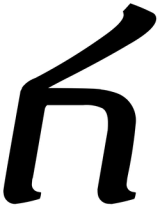


























































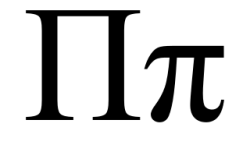














































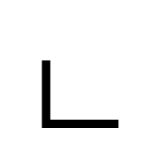






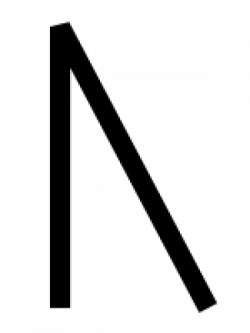






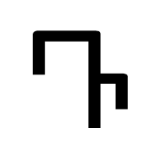






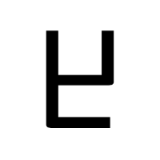





















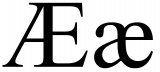




Have a discussion about the Alphabets group with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In